Topic 6
Forecasting
Chapter 9 in Core Text
Key points in this chapter :
Ñ Need for Forecasting
Ñ Methods of Forecasting
Ñ Qualitative Methods
Ñ Quantitative Methods
Ñ Measurement of Trend
The Need for Forecasting
The increasing complexity of the environment in which organisations have to function and survive, together with changing demands and expectations, implies that every organisation needs to establish some view as to future values of key variables, even though these key variables are different for different organisations.
As with other techniques, forecasting is primarily concerned with trying to reduce the uncertainties that exists about some part of the future. Managers in an organisation hope that by applying some forecasting technique they can generate additional information about the future that may help them assess the future consequences of existing decisions and to evaluate the consequences of alternatives.
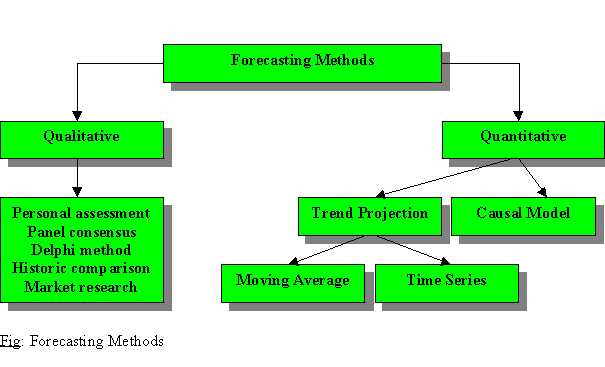
Methods of Forecasting
Depending on the variables being forecast, the methods adopted for forecasting and the perceived accuracy of the forecasts, such information may also affect the strategy formulation process itself. The organisation will clearly need to establish some monitoring system to compare planned performance with the actual performance. The alternative methods of forecasting can be divided as follows:

Qualitative Methods
1. Personal assessment
Based on his or her own judgement, an individual produces some forecast of the future situation. In some circumstances such an assessment can be relatively reliable and accurate. It is particularly appropriate in an operational environment when asking the front line staff their view of the immediate future: whether a particular machine will need repair or maintenance in the next month., whether stock levels are likely to last until the next delivery takes place etc.
2. Panel Consensus
Such an approach collects together a group of individuals and in a structured format tries to develop a shared idea of the view among the group, encouraging them to share information, opinions and assumptions. The difficulty with such an approach, however, is that it is very dependent on group dynamics and frequently requires a skilled facilitator to 'manage' the process of developing a consensus.
3. Delphi Method
In the Delphi method the experts never actually meet and usually do not know who the other panel members are. Each expert is given an initial questionnaire to complete relating to the area under investigation. A summary is then produced from all the questionnaires and this summary is then distributed to each expert who is given the opportunity of revising the responses to the questionnaire in the light of this summary of the group's views. This process is repeated until either an adequate consensus is reached or an agreed number of iterations completed. Typically, the Delphi method is used to produce a narrow range of forecasts rather than a single view of the future.
4. Historic Comparison
Under limited circumstances it may be possible to produce forecasts based on observed patterns of some similar variable in the past. Many products and services, for example, will tend to follow the life-cycle process.
5. Market Research
Quite often businesses carry out various market research activities inorder to predict the shape of the future things to come. For example, market research could be carried out by car manufacturers to determine the features that car buyers would want to have in their cars. Accordingly, cars could be manufactured to meet the demands and expectations of the consumers.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods tend to fall into two general categories:
1. Causal methods
When two or more variables share a cause and effect relationship, it is easy to predict the changes in one variable on the basis of the changes in the other. For example, we know that the price of and demand for a product share a inverse relationship i.e if the price of a product goes up, the demand for the product will go down and vice-versa. Thus, when the cause and effect relationship between two or more variables is known, it is easy to predict the changes in one variable based on the changes in the other. If we even know the degree of resulting changes that take place, we can pinpoint with greater accuracy the resulting effect in the other variable.
2. Trend Analysis
Trends or variations could be divided into four types::
a) Secular trend: secular trends are attributable to factors such as population changes, technological progress and large-scale shifts in consumer tastes.
b) Cyclical trend: cyclical fluctuations are long-term movements that represent consistently recurring rises and decline in activity. A business cycle consists of the recurrence of the up and down movements of business activity categorized into prosperity, decline, depression and recovery.
c) Seasonal trend: although the word 'seasonal' seems to imply a connection with the season of the year, the term is meant to include any kind of variation which is of periodic nature and whose repeating cycles are of relatively short duration. The factors that may cause seasonal variations are climate and weather conditions, customs, traditions and habits of people etc.
d) Irregular trend: also called 'erratic' variations, these refer to changes in business activity which do not repeat in a definite pattern. It includes all types of variations other than those accounting for the trend, seasonal and cyclical movements. Irregular trends are the result of chance factors such as floods, earthquakes, strikes, wars etc.
Measurement of Trend
The various methods that can be used for measuring trend are:
1. Freehand or graphic method
2. Semi-average method
3. Moving average method
4. Method of least square
Decision-Making Academic Homepage