Topic 9:
TEAMWORK
Chapter 18 in Text Book
Pages: 496 - 521
Key topics in this chapter :
Ñ Teamwork in Management
Ñ What is a Team
Ñ Types of Teams
Ñ Stages of Team Development
Ñ Why use Teams
Ñ Characteristics of Effective Teams
Ñ Managing Conflict
Ñ Future Growth of Teams
Teamwork in Management
Ever since time memorial man has been trying to find newer and better ways of organizing things. This need for organizing things and even people arises due to the benefits that simplicity and systematization creates in the environment. Such organizing efforts can also be seen in business organisation which continuously strive to achieve their goals and objectives through an effective management. Management is an art and it comprises of various functions like planning, organizing, leading and controlling. Inorder to carry out all the above functions, managers often make use of a way of grouping people into small units which are called Teams.
What is a Team
A team is defined as two or more people who interact and influence each other towards a common purpose. Organisations function with a common goal in mind and there should be a unity of direction and efforts of the people working in an organisation. Inorder to promote this unity and to create a synergy in the organisation, employee's social needs are understood and their needs for affiliation are satisfied by the formation of various types of teams in the organisation.
Types of Teams
Teams can be broadly classified into Formal and Informal Teams
Formal Teams are deliberately created by managers charged with carrying out special tasks. These types of teams are created based on the formal organisation structure and are formed to achieve the organization's goals and objectives. A formal team can be of three different types.
1. Command Teams comprises of a manager and all employees reporting to that manager. For example, a marketing manager and all his subordinates working under him are collectively called a command team as they have a command over the marketing department.
2. Committees are a formal organisational team, which are usually relatively long lived and which deal with specific problems and decisions. For example, it can often be seen in organisation that an employee grievance committee is formed to look into employee's complaints and problems and to devise solutions for those problems.
3. Task Forces (Project Teams) are created to deal with a specific problems in case of emergencies or changes in an organization. For example, if an organisation plans to set up a branch in a foreign location, then they might set up a project team to look into the various aspects of the foreign location and this team will then suggest to the management the right strategy for setting up the foreign branch.
Informal Teams emerge when people come together and interact regularly. The need for such team arises as a result of employees social needs and needs of belongingness. Such teams strengthen norms and values that members hold in common. It gives members a feeling of social security, status and satisfaction. Helps members communicate more freely and thus solve problems. An informal team can be of two different types.
1. Interest Groups (E.g. Hobby, Sports ) are formed to facilitate employees pursuits of common concern
2. Friendship Groups (E.g. On Picnics) are formed to meet employees social needs of association.
Self Managed Teams : Super teams are teams that manage themselves . The whole team takes the responsibility of achieving the "complete task at hand". Members possess a variety of skills and they themselves decide their goals, schedules and methods of performance. Moreover the performance of the whole team forms the basis for compensation and feedback.
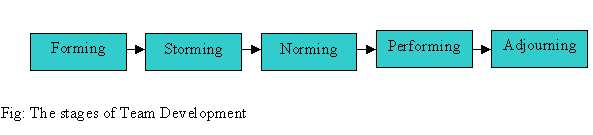
Stages of Team Development
The process of team development takes place through a series of steps which are as follows:

1. Forming: During this stage the members of the group get to know one another and various rules and regulations are set about the general beahvioural patterns within the team. The team members tend to interact informally in the beginning so that they get acquainted and understand their own initial position vis-à-vis others in the same team and other teams as well. Moreover, the importance of their group goals is highlighted so that the team remain cohesive towards the achievement of the group goals.
2. Storming: During this stage some members oppose the structure of the team and may even protest against the rules and regulations set during the forming stage. Some members disagree with other members in the team due to conflicts arising out of various reasons like conflicts in the roles assigned, conflicts in the power structures or even conflicts arising out of personality disputes. During this stages it is quite possible that some members may form their own 'in-group' within the team. It is therefore essential that conflicts or any misunderstandings are resolved at this stage itself and that they are not allowed to escalate further.
3. Norming: The conflicts and differences are then sorted out and after negotiation with other members acceptable rules and standards are set. Having accepted the negotiated rules everyone in the team now becomes more comfortable and speaks more confidently thus developing close and strong relationships. It should however be noted that it is not merely the development of trustworthy relations that is important in a team. A team is set with a particular purpose in mind and it can be achieved only when the team actually starts performing.
4. Performing: Members are now ready to direct their efforts towards the achievement of group goals and each member in the team becomes a valuable asset for the total performance of the team. It should be remembered that even during this stage, conflicts may arise between the team members but the conflict at this stage is positive and functional. It helps the team members work towards the achievement of their goals in a
more creative manner. Members learn to understand each other's view point more openly and constructive feedback is provided about each team member's performance.
5. Adjourning: Finally, after the teams goals are reached they wrap up all activities and then the group ceases to exist. This may lead to feelings of joy (as the goals are achieved ) or feelings of depression (as the members are now no more part of that same team ). However, it should be understood that some teams are set up for a very small period of time while others are set up for an indefinite period and though the members might change the team may exist throughout the life of the organization. It should be remembered that the team should acknowledge their end results. After monitoring the results the team should try to find out the causes of the errors (if any) or should celebrate their achievements.
Why use Teams
· Organisations use various forms and types of teams as it helps promote the feelings of unity and promotes cohesiveness within the group.
· By working upon a certain specific issue teams can give their best to the task at hand and this way managers can allocate different decisions to different teams thus promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
· As a team may comprise of members from different backgrounds (age, gender, qualifications, culture, education etc. ) they tend to look at the same issue with varying angles of perception and this brings creativity to the solution of problems.
· The combination of two or more individuals in a team helps bring about synergy.
Example: At Boeing Company, technology and people are keys to the development of the new 777. Designs for the 777 airplane utilize the latest computer assisted techniques and are largely paperless. Engineers work out problems on powerful computers, including all the coordinating details of over 130,000 engineered parts and more than 3 million rivets, screws, and fasteners. But technology doesn’t stand alone, people count too. Engineers work in a team structure where cross-functional "design-build" teams include representatives from all areas, whose contributions are essential. Design and manufacturing problems are to be solved by the teams before production starts. Each team is thought of as little companies who have individual cost and performance targets.
Characteristics of Effective Teams
Inorder to be effective a team should have the following characteristics :
· Clear understanding of the team goals, what is to be accomplished by each member and how.
· Inorder to achieve the goals smoothly the team members should comprise of members who have the relevant skills. The skills should not only be technical or professional but also interpersonal, social and communication skills.
· The team members should have trust in themselves and also between themselves. Only a mutual trust can help them to remain strongly unified.
· Conflict is not suppressed. Team members should be allowed to express negative feelings and confrontation within the team which is managed and dealt with by team members. Dealing with and managing conflict is seen as a way to improve team performance.
· Each member of the team should be committed to achieving the group goals.
· There should be good communication between every member and every member should be given an opportunity to voice their concerns, ideas, suggestions etc. There should be cohesiveness in a team.
· The team should also be supported by other teams to have the right coordination and moreover all the teams should be integrated by the organization's management.
· Every team should also have an appropriate leader and he/she should guide the team using the right style of leadership.
Example: Enthusiasm and high-performance norms rule the day at Motorola's Penang, Malaysia, operation. A team spirit rallies the plant's workers who in one year alone submitted 41,000 suggestions for improvement and saved the firm some $2 million. Now Motorola is trying to import the Malaysian team spirit to it's Florida operation. New applicants are carefully screened for their attitudes towards teamwork. A quality team at the Florida plant suggested ways to streamline workflow and increased output by 150 %.
Managing Conflict
One of the most important area where management's attention is required is towards the management of conflict that takes place both within a team and between teams. Conflict, if unchecked can create a lot of damage to the performance of the team. However, not all types of conflict is harmful. Infact if there is no conflict or competition between the teams then the teams performance may actually be lower. It is the job of the management and the team leaders to utilize this conflict in a creative manner and use it towards the betterment of the group.
Future Growth of Teams
The development of teams play a very important role in the successful management of staff in an organisation. Teams when utilized constructively can be used to promote creativity and unity in an organisation and can help in the development of the entire organization's cohesiveness. Team members then start viewing themselves less as individuals and more as part of the entire group. It should be remembered that the formation of teams may result in conflicts at times as people are bound to clash due to communication, structural or even personality differences. However, such conflicts are normal in any team and it is the job of the manager to ensure that conflict is used positively and that it does not obstruct the team's performance.
Today, teamwork is being promoted in most organisations because they permit faster decision making and facilitate cultural diversity in the workplace. The growth of virtual teams, where members work together and solve problems through computer based interactions, has made newer accomplishments possible. Managing teams effectively involves all the managerial functions of planning, organizing, leading and controlling. Planning issues for teams include having clear goals. Organizing issues include clarification of authority and structural relationships. Leading issues include what role the leader will play and controlling issues involve appraisal and reward system for the team. Only such an integrated approach can help management ensure their organization's continued mastery through the successful use of teams.
Test Your Knowledge
& A _____ is defined as two or more people who interact and influence each other towards a common purpose or goal.
& Teams may be broadly classified into __________ and ____________.
& A _________ team is created based on the formal organisation structure.
& A finance manager and all his subordinates taken collectively is an example of a ______ team.
& A _______ is created to address a specific problem that an organisation faces.
& Informal teams are created because of people's social needs (True or False)
& Two types of informal teams are ________ and ________
& Members of a _________ team possess a variety of skills.
& Self-managed teams may not necessarily require a __________
& Forming is the first stage in the development of teams (True or False)
& Conflicts and differences in a team are settled in the _________ stage of development.
& Teams help promote ________ and _________ in an organisation.
& The combination of two or more individuals as a team helps bring _______ in an organisation.
& All types of conflicts should be suppressed in a team (True or False)
& Expectations about how members will perform are called ______
& In _______ teams members work together and solve problems through computer based interactions.
& There should be cohesiveness within teams and not between teams (True or False)