Topic 4:
PLANNING
AND
DECISION MAKING
Chapter 9 and 10 in Text Book
Pages: 237 - 283
Key topics in this chapter :
Ñ What is Planning
Ñ Features and Importance of Planning
Ñ Levels of Planning
Ñ Types of Plans
Ñ Steps in the Planning Process
Ñ Limitations of Planning
Ñ Decision Making
Ñ Steps in Decision Making
Ñ Strategic Management Process
What is Planning
"Planning is a pervasive and continuous executive function involving complex processes of perception, analysis, communication, decision and action."
"Planning is the design of a desired future and of effective ways of bringing it about."
Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done, where it is to be done and who is to do it. It is a process of thinking before doing. Planning implies that managers think through their goals and objectives chalked out in advance. Planning is the process used by managers to identify and select goals and courses of action for the organization. The organizational plan that results from the planning process details the goals to be attained.
Features and Importance of Planning
Features
· Planning is goal-oriented
· Planning precedes all other functions of management.
· Planning is applicable at all levels and all types of organisations.
· Plans can be changed as and when the environment requires.
· Planning continues throughout the lifetime of an organisation.
· Planning looks ahead into the future
· Planning involves choosing between various alternative courses of action
· Planning involves insight, intelligence and other creative characteristics.
Importance
· Planning makes objectives clear and specific
· Planning makes activities meaningful
· Planning reduces the risk of uncertainty
· Planning facilitates decision making
· Planning helps coordination
· Planning promotes creativity
· Planning provides the basis of control
· Planning leads to economy and efficiency
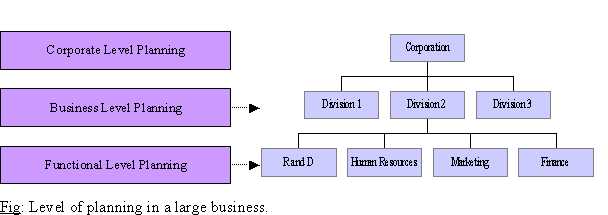
Levels of Planning

Corporate level planning directs what the organisation should pursue as a total enterprise. Decisions by top managers. Considers on which business or markets to be in. Provides a framework for all other planning
Business level planning guides how the organisation will compete in each major business. Details divisional long-term goals and structure. Identifies how this business meets corporate goals. Shows how the business will compete in market
Functional level planning explains how each management functions will support the business. Actions taken by managers in departments of manufacturing , marketing etc. These plans state exactly how business level strategies are accomplished
Types of Plans
On the basis of:
Breadth:
· Strategic: a comprehensive plan that addresses the long term needs and direction of the organisation.
· Operational: plans that provides the details needed to incorporate strategy into day to day operations.
Time Frame:
· Long Term: long-term plans are usually 5 years or more.
· Short Term: short term plan are for a period of less than 1 year
Frequency of use:
· Single Use: a detailed course of action used once or only occasionally to solve a problem that does not occur repeatedly.
· Standing Plans: an established set of decisions used by managers to deal with recurring activities. Major types of standing plans are:
· Policies: a standing plan that establishes general guidelines for decision making.
· Rules: standing plans that detail specific actions to be taken in a given situation.
· Procedures: a standing plan that contains detailed guidelines for handling organisational actions that occur regularly.
Functions:
Plans may also be classified according to the type of the function/department in which they are intended to be used. Thus on the basis of function, plans may be divided into:
· Marketing
· Finance
· Operations etc.
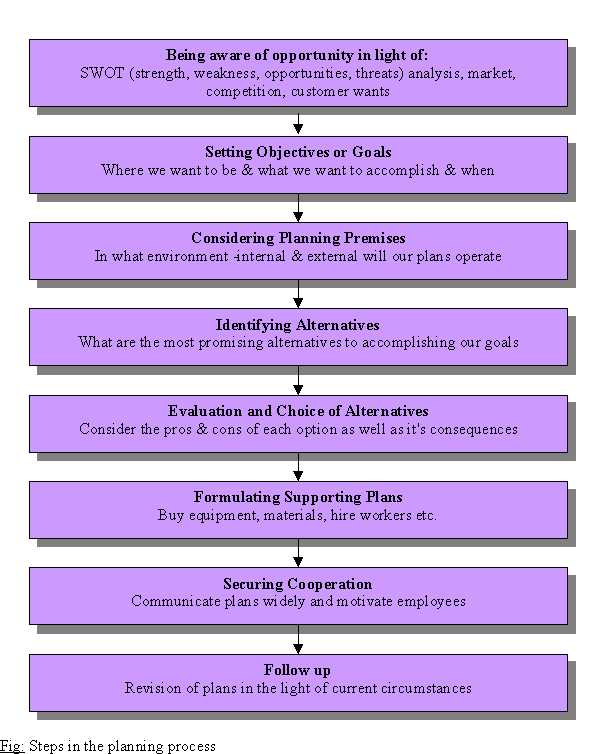
Steps in the Planning Process
Limitations of Planning
· Planning may create rigidity in the minds of managers.
· A faulty plan may actual misdirect the organisation
· Planning often involves a lot of time, effort and money.
· Planning may create a false sense of security that everything is moving according to plans
· Planning is based on probability and forecasts may go wrong.
How to overcome the limitations
+ Involve the right people in the planning process
+ Write down the planning information and communicate it widely
+ Goals and objectives should be SMARTER (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-framed, enhancing and rewarding)
+ Build in accountability - make clear who is responsible for what.
+ Note deviations and re-plan accordingly
+ Continuously evaluate planning process and plans
+ Acknowledge results, whether good or bad and celebrate good results
Apart from the various suggestions listed above, to overcome the limitations of planning, organisations should also try to use newer and better approaches and techniques in the planning process. Some of these include Forecasting, Scenario Planning, Benchmarking, Management by Objectives (MBO), Participation and Involvement.
Decision Making
Decision making may be defined as the process of identifying and selecting a course of action to solve a specific problem. A problem is a situation that occurs when an actual state of affairs is different from a desired state of affairs. Problems may be under circumstances of Certainty, Risk or Uncertainty.
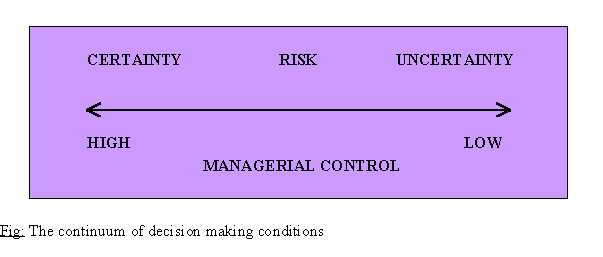
Certainty: decision making condition in which managers have accurate, measurable and reliable information about the outcome of various alternatives under consideration.
Risk: decision making condition in which managers know the probability a given situation will lead to a desired goal or outcome.
Uncertainty: decision making condition in which managers face unpredictable external conditions or lack the information needed to establish the probability of certain events.
Depending on the nature of the problem and the level in the organisation managers may take programmed or non-programmed decisions. Programmed decisions are repetitive decisions that can be handled by a routine approach. Non-programmed decisions are unique decisions that require a custom-made solution.

Decision Making is influenced by Rationality, Bounded rationality, Satisficing or Heuristic principles.
Steps in Decision Making
· Identification of a Problem:
We need to make a decision something as there is a problem that is causing some obstacles towards the achievement of our goals smoothly.
· Identification of decision criteria:
We need to think about the various factors that can influence our choice or those factors that we consider important in our decision.
· Allocation of weights to criteria:
All the factors thought of may hold the same importance, hence it necessary to allocate weights to each of the factors on the basis of their relative importance.
· Development of alternatives:
Having allocated appropriate weights we need to consider the various alternatives that are available to us.
The alternatives identified should then be analyzed with respect to the factors that we decided earlier
· Selection of an alternative:
From the various alternatives identified we need to select an alternative that best matches our criteria
· Implementation of the alternative:
The alternative finally chosen is then implemented .
However the decision making process doesn’t end here. We also need to evaluate the effectiveness of our decision and should learn from our current decisions to make better decisions in the future.
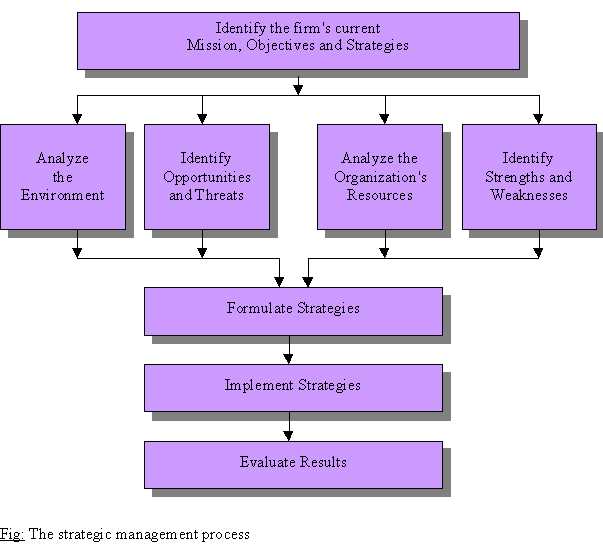
Strategic Management Process
The pattern of decisions managers take to reach the organisational goals is the organization’s strategy. The planning function determines how effective and efficient the organization is and helps setting the strategy of the organization.
MISSION: Overriding premise in line with values of the stakeholders.
GOAL: General statement or aim of purpose
OBJECTIVES: Quantification or more precise statement of the goal
STRATEGIES: Broad action plans to achieve the goals
ACTION: Individual steps to implement strategies
CONTROL: Monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of strategies
REWARDS: A payoff for reaching the objectives.
Example
The America West Airlines corporate mission reads "America West will support and grow it's market position as a low-cost, full-service nationwide airline. It will be known for it's focus on customer service and it's high performance culture. America West is committed to sustaining financial strength and profitability, thereby providing stability for it's employees and shareholder value for it's owners.
British Airways' mission is "to be the best and the most successful company in the airline industry.
Skyline College's mission is to provide it's students with the best professional career prospects in the emerging global market place and to equip them to become effective business managers.
Example: When Howard Schultz joined Starbucks in 1982 the firm was a small coffee retailer in Seattle. But Schultz saw more potential that included Starbucks becoming a national chain of stores offering the finest coffee drinks. Today Starbucks has grown to ver 2,300 stores cross North America and is expanding internationally towards it's goal of becoming the most recognized and respected brand of coffee in the world. All this was possible through a long term vision and effective strategies laid down by the management.
The strategic management process is explained in the diagram below:
Test Your Knowledge
& ______ implies that managers think through their goals and decisions chalked in advance.
& Planning is required only at the time of setting up business (True or False)
& Planning makes _______ clear and specific
& The three levels of planning are _______, __________ and ____________.
& The first two important functions of management are ______ and _________.
& A general plan which outlines the long term needs and direction of an organisation is called __________
& Short term plans are usually for a period of 5 years (True or False)
& A detailed course of action used once to solve a problem that does not occur repeatedly. (Name the concept)
& Plans developed for activities that recur regularly over a period of time are called ______
& A standing plan that establishes general guidelines for decision making is called _______
& Securing cooperation is not an important step in the process of planning (True or False)
& Faulty plans affect the success of the whole organisation (True or False)
& _________ may be defined as the process of identifying and selecting a course of action to solve a specific problem.
& A ______ is a condition in which managers know the probability of a given situation leading to a desired goal or outcome.
& Decisions may be divided into ________ and _______ depending on the nature of the problem and the level in the organisation.
& The decision making process involves allocating weights to various alternatives and choosing the best alternative (True or False)
& An overriding premise in line with the values of the stakeholders is called a ________.
& _________ are broad action plans to achieve the goals.
& Implementing strategies is not a part of the strategy management process (True or False)