Topic 1
Introduction to Decision Making
Chapter 1 in Core Text
Key points in this chapter :
Ñ What is Decision Making
Ñ Programmed and Non Programmed Decisions
Ñ Structured and ill-Structured Decisions
Ñ Steps in Decision Making Process
Ñ The Strategic Management Process
Ñ Phases of Decision Making
Ñ Factors affecting Managerial Decision Making
Introduction
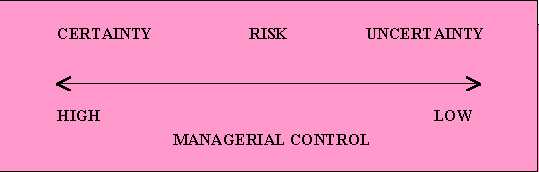
Decision making may be defined as the process of identifying and selecting a course of action to solve a specific problem. A problem is a situation that occurs when an actual state of affairs is different from a desired state of affairs. Problems may be under circumstances of Certainty, Risk or Uncertainty.

Fig: The continuum of decision making conditions
Certainty: decision making condition in which managers have accurate, measurable and reliable information about the outcome of various alternatives under consideration.
Risk: decision making condition in which managers know the probability a given situation will lead to a desired goal or outcome.
Uncertainty: decision making condition in which managers face unpredictable external conditions or lack the information needed to establish the probability of certain events.
Depending on the nature of the problem and the level in the organisation managers may take programmed or non-programmed decisions. Programmed decisions are repetitive decisions that can be handled by a routine approach. Non-programmed decisions are unique decisions that require a custom-made solution.
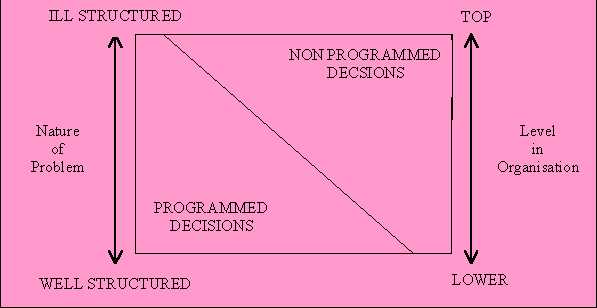
Fig: Type of decision with regard to the nature of problem and level in the organisation.
Decision Making is influenced by Rationality, Bounded rationality, Satisficing or Heuristic principles.
Steps in Decision Making
· Identification of a Problem:
We need to make a decision something as there is a problem that is causing some obstacles towards the achievement of our goals smoothly.
· Identification of decision criteria:
We need to think about the various factors that can influence our choice or those factors that we consider important in our decision.
· Allocation of weights to criteria:
All the factors thought of may hold the same importance, hence it necessary to allocate weights to each of the factors on the basis of their relative importance.
· Development of alternatives:
Having allocated appropriate weights we need to consider the various alternatives that are available to us.
· Analysis of alternatives:
The alternatives identified should then be analyzed with respect to the factors that we decided earlier
· Selection of an alternative:
From the various alternatives identified we need to select an alternative that best matches our criteria
· Implementation of the alternative:
The alternative finally chosen is then implemented .
However the decision making process doesn’t end here. We also need to evaluate the effectiveness of our decision and should learn from our current decisions to make better decisions in the future.
Strategic Management Process
The pattern of decisions managers take to reach the organisational goals is the organization’s strategy. The planning function determines how effective and efficient the organization is and helps setting the strategy of the organization.
MISSION: Overriding premise in line with values of the stakeholders.
GOAL: General statement or aim of purpose
OBJECTIVES: Quantification or more precise statement of the goal
STRATEGIES: Broad action plans to achieve the goals
ACTION: Individual steps to implement strategies
CONTROL: Monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of strategies
REWARDS: A payoff for reaching the objectives.
Example
The America West Airlines corporate mission reads "America West will support and grow it's market position as a low-cost, full-service nationwide airline. It will be known for it's focus on customer service and it's high performance culture. America West is committed to sustaining financial strength and profitability, thereby providing stability for it's employees and shareholder value for it's owners.
British Airways' mission is "to be the best and the most successful company in the airline industry.
Skyline College's mission is to provide it's students with the best professional career prospects in the emerging global market place and to equip them to become effective business managers.
Example: When Howard Schultz joined Starbucks in 1982 the firm was a small coffee retailer in Seattle. But Schultz saw more potential that included Starbucks becoming a national chain of stores offering the finest coffee drinks. Today Starbucks has grown to ver 2,300 stores cross North America and is expanding internationally towards it's goal of becoming the most
recognized and respected brand of coffee in the world. All this was possible through a long term vision and effective strategies laid down by the management
Phases of Decision Making
Phase 1: Identification
Recognition of the problem
Diagnosis of the problem
Phase 2: Development
Searching existing solutions
Modifying existing solutions
Designing new solutions
Phase 3: Selection
Judgement by managers
Logical analysis
Decision-Making Academic Homepage