Topic 3:
ORGANISATION'S ENVIRONMENT
Chapter 3 in Text Book
Pages: 60 - 94
Key topics in this chapter :
Ñ What is Environment
Ñ External Environment
Ñ Internal Environment
Ñ Natural Environment
What is Environment
An organization does not exist in a vacuum. It exist in an environment. An environment can be defined as the sum total of all the surroundings under which an organisation exists. An organisation performs it's various activities by taking various inputs from outside, processing these inputs and then providing them to the outside world in the form of outputs (goods, ideas or services). Similarly, such systems take place in every organisation and all these organisation are collectively a part of a much bigger system.
There are various factors that influence the functioning of the organization's activities and these factors can be broadly divided into external and internal environmental factors.
External Environment
External environment includes those factors that influence all the organisations in a country irrespective of their type of activity, size, number of employees, volume of turnover etc. These factors are also known as the Indirect-action elements as they do not affect the organisation directly. These factors include the following:
Social : These include factors like the culture (values, norms, beliefs) of the people where the organisation is located, the relationship between people and different groups, the buying habits of people, the role of men and women, the lifestyles that different groups adopt and also the demographic situation of the place. Demographic factors play a very important role as they help organisations decide what the total market is for their product/service, how the total population is changing, what is the composition of the population and also what the likely future trends are.
Example: When British Airways surveyed it's customers a simple lesson emerged - don’t assume that people from different cultures will have the same dining habits and preferences. Japanese, for example, commented that BA's food was not bad for westerners. They also pointed out that the white china dishes were similar to those used in Japanese hospitals and prisons ! Thus BA initiated a major overhaul to get a more truly global identity.
Similarly McDonalds, when entering India had to consider the fact that it would save serious problems if beef was not included in it's menu as eating beef is considered irreligious among the majority Hindu population. Accordingly it tried to popularize Veg Mc in India. And the same company promotes the burger with wine in France due to French's preference for wine with meals.
Legal : All the organisation existing with the boundaries of a country have to follow the laws that have been laid down in that country. These include various mercantile laws, contract laws, labour laws etc. Such laws apply to all types of organisations; however there might even be laws that cover certain specific types of organizations or industries.
Example: Organizations involved in fisheries and those dealing with hazardous chemicals and dangerous goods have to face strict pollution, safety control laws.
Economic : Various economic conditions are crucial to the success of any organisation. The wage level in the country, the rate of inflation, fiscal and monetary policies undertaken by the central bank, the level of growth in the national income, personal disposable income etc all have a strong influence on the activities that any organisation takes. Any changes in these factors will has to be carefully monitored by organisations.
Political : The political scenario in the country - the type the government (majority, coalition), political stability/instability, the prospects of war etc. all affect an organization's growth and their activities with other organisations throughout the world. Moreover, it is the government that shapes the various economic and legal forces in the country.
Technological : It includes the various advances and developments that place in technology which help in improving the products or services offered by organisation. It not only includes innovations in the field of materials but also includes other developments in the product design, processes, distribution, promotion techniques etc. Such changes often make products or processes obsolete very quickly and therefore management should be prepared to change.
Example : The introduction of EPOS (Electronic Point of Sale) system that is being widely used in retail stores throughout the world. The developments in the field of bio-technology has also brought about the introduction of GM (Genetically Modified) foods.
Another example that highlights the role of technology in management of operations is E-banking. It has been researched that online banking is 97 % cheaper that ATMs and 99% cheaper that human tellers. Moreover, it also provides a platform for local banks to target foreign customers who couldn’t use the services earlier due to geographical barriers. E.g. ICICI, ME Bank.
These external forces have a profound impact on the organisations and managers usually cannot control these.
Apart from the above five forces in the external environment organisations also have to consider the Global Forces arising out of a change in the international relationships between countries. Perhaps the most important is the economic integration of countries at various levels . (E.g. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), North American Free Trade Association (NAFTA) European Union (EU), Gulf Co-Operation Council (GCC) etc.
All the forces in the environment can change overtime and thus provide Opportunities or Threats to organisations. Opportunities are new openings for managers to enhance revenues or open new markets through new technologies, new ideas etc. Threats are issues that can harm an organisation success or even it's very survival.
Internal Environment
Apart from the various external environmental factors there are various factors that directly influence an organization's activities. These are also known as the Direct-action elements. They include :

Stakeholders are individuals or groups who are directly or indirectly affected by an organization's pursuits of it's goals.
Internal Stakeholders: An organisation is responsible towards it's internal stakeholders which are the employees and the shareholders (people who have invested their money into the business). The organisation has to make sure that the employees get a fair wage/salary, have proper work conditions and that they receive adequate opportunities for growth and development in the organisation. At the same time an organisation also has to ensure that the shareholders get a good return on their investment.
Example: Many people said that Aaron Feurstein was crazy when he kept some 1000 workers in the payroll after his apparel factory burned down. Today Malden Mills of Lawrence, Massachusetts is back in business and the owner couldn’t be prouder. He paid his jobless employees over $15 million during the several months it took to rebuild the plant. Now he is reaping the gains of a loyal workforce dedicated to their customers. Feurstein calls his decision just "common sense".
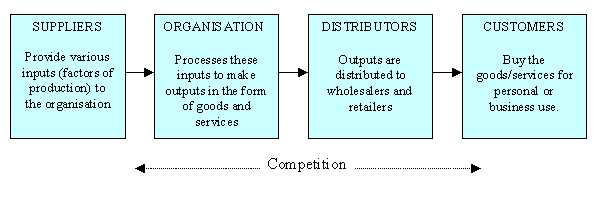
External Stakeholders : stakeholders that affect an organization's activities from outside the organisation include suppliers, distributors, customers, competitors and other elements. Their relationship with the organisation can be seen in the diagram below:
Apart from these core elements of the direct stakeholders there are competitors in any business too. An organisation has to make sure that they effectively check their Competitors activities, their new products, their prices etc.
Example: Competition plays a key role in the "burger wars". Soon after Burger King introduced it's version of the McDonald's "Big Mac" sandwich, McDonald's offered something quite similar to Burger King's "Whopper" The tendency among fast food makers is towards an outside-in strategy of "If you can't beat them, copy them" !
Similar intense competition or rivalry can be seen in almost every industry. The success of "Kaun Banega Crorepati" (a TV game show based on the popular English show "Who wants to be a millionaire" ) on Star TV was soon copied by Zee TV with it's launch of "Sawal Dus Crore Ka" and was further copied by Sony Entertainment Television's "Jeeto Chappar Phaad Ke". Apart from these shows there were also similar 'jackpot' shows on various regional channels too.
Competition may not only be on the product (introducing similar products), but also on the process (using similar techniques for production) people (though difficult to copy as people are unique but organisation at times copy other organization's training programs or even go a step further and entice competitor's employees to join their organisation, in return for better
pay and perks) or even on promotion (often seen in the similar advertisements or the promotional campaigns amongst the giants of the cola war - Pepsi and Coke)
Other elements that are playing an increasing role in modern businesses include the labour unions and consumer protection groups. Different Labour Unions exist among different categories of work and even at the state and national levels.
Similarly, the modern educated consumers now no longer tolerate any exploitation by the organisations and have formed various Consumer Protection Groups to deal with any issues of consumer exploitation.
Natural Environment
Today organisations have also to consider the various impacts that their operations are bringing about on the country's (and the world's) Natural Environment. The increasing air pollution by factories, depletion of ozone layer, cutting down of forests, water pollution through oil slicks, improper factory waste disposal, animal testing etc all are being monitored by the government and community at various levels to ensure that organisations follow an image of "Green and Clean".
Example: Recycling car parts is the goal of the RAT pack at the Ford Motor Company. The firm's Recycle Action Team meets once a week to find new ways to use recycled materials and to recycle as much as possible of the firm's products. Ford vehicles now are incorporating parts made from recycled tires, soda bottles and even used carpeting from homes. A special project of Ford's environmental outreach and strategy program. RAT is a good example of applying team creativity and initiative to solve important problems.
Test Your Knowledge
& An _________ is the sum total of all the surroundings under which an organisation exists.
& The environmental factors that an organisation faces can be divided broadly into ________ and _________.
& External factors affect all organisations in the same manner (True or False)
& External environment is also known as _________________
& Factors like culture, lifestyle, religion etc are collectively called _______ factors.
& The laws of a country do not affect organisations. (True or False)
& Economic factors include _________, _________ and _________.
& Changes arising out of international relationships between countries is called __________
& The forces in the external environment may provide an ________ or a ________ to the organisations.
& The internal environment in other words is known as the direct-action elements (True or False)
& ____________ are individuals or groups who are directly or indirectly affected by an organization's pursuits of it's goals.
& Internal stakeholders include __________ and ___________
& Stakeholders that affect an organisation from outside the organisation are called _________ stakeholders.
& Suppliers, distributors, customers, competitors are examples of external stakeholders (True or False)
& Today organisations also have to be concerned about the _________ environment inorder to project a clean and green image.