Topic 6:
LEADING
Chapter 17 in Text Book
Pages: 468 - 495
Key topics in this chapter :
Ñ Meaning of Leadership
Ñ Power
Ñ Approaches to Leadership
Ñ Trait Approach
Ñ Behavioral Approach
Ñ Contingency Approach
Ñ Functions and Responsibilities of a Leader
Ñ Other Issues in Leadership
Ñ Leadership across Cultures
Meaning of Leadership
Leadership involves a manager using power, influence, vision, persuasion, and communication skills. It may be defined as the process of directing and influencing task related activities of group members. In leading, managers determine direction, state a clear vision for employees to follow, and help employees understand the role they play in attaining goals. Leadership involves influencing people through the use of different types of power.
Leadership = Respect x Trust
Respect is based on knowledge and skills while trust is based on concern for people's needs and feelings
Show respect for others….
People will respect you only when you show that you respect them. Treat people as individuals, seek their opinions and listen to their suggestions. If you are willing to listen and take other people's inputs seriously, they will be more willing to listen to you and take your input seriously.
Respect….know you job and do it well. People respect knowledge. When you answer people's questions correctly and can explain why certain procedures are important, you are demonstrating your knowledge and showing people that you know what you are talking about.
Be fair…you are a human being and you have your own likes and dislikes. Your personal feelings should never influence your treatment of people. Every person you work with deserves fair and equal treatment when work is assigned and performance is evaluated . you should be consistent in the way you treat people. Do not be moody, or treat people based on how you feel.
Trust….you can build trust by using positive and corrective follow up, by showing that you care, by creating a positive working environment, by treating people the way you like to be treated. Get to know people….you need to know your staff well to build trust so that they realize that you don’t think of them merely as employees.
Power
Power is the capacity to affect the attitudes or behavior of others. It is the ability to get someone else to do something you want done or to make things happen the way you want.
Sources of Power: The sources of power may be broadly classified into two sets.
1. Position Power: An important source of power is a manager's official status, or position in the organization's hierarchy of authority. The three bases of position power are:
· Legitimate power: the capacity to influence other people by virtue of formal authority or the rights of office.
· Reward power: the capacity to offer something of value as a means of influencing people.
· Coercive power: the capacity to punish or withhold positive outcomes as a means of influencing other people.
2. Personal Power: Another source of power is the manager's unique personal qualities that he brings to a leadership situation. Two bases of personal power are:
· Expert power: the capacity to influence other people because of specialized knowledge.
· Referent power: the capacity to influence other people because of their desire to identify personally with you.
Another source of power that is also visible if "Access to Information" power It is the capacity to influence people because of access to company information, strategic plans etc.
|
Power of the POSITION Based on things managers can offer to others |
Power of the PERSON Based on ways managers are viewed by others
|
|
Rewards: "If you do what I ask, I'll give you a reward" |
Expertise - as a source of special knowledge and information. |
|
Coercion: "If you don’t do what I ask, I'll punish you." |
|
|
Legitimacy: "Because I am the boss, you must do as I ask" |
Reference - as a person with whom others like to identify. |
Fig: Sources of position and personal power used by managers
Approaches to Leadership

Trait Approach : This approach believes that leadership behavior is the sum total of all the traits (qualities) of the leader. Psychologists studying leadership behavior have classified these traits into:
Physical characteristics like height , weight, appearance….
Personality characteristics like intelligence, knowledge…
Social factors like inter personal skills, socio-economic position….
Six Traits that differentiate leaders from non leaders
1. Drive: leaders exhibit a high effort level. They have a relatively high desire for achievement, they're ambitious, they have a lot of energy, they're relatively persistent in their activities and they show initiative.
2. Desire to lead: leaders have a strong desire to influence and lead others. They demonstrate the willingness to take responsibility and are always enthusiastic and motivated to perform at their best level.
3. Honesty and integrity: leaders build trusting relationship between themselves and followers by being truthful or non deceitful and by showing high consistency between work and deed.
4. Self-confidence: followers look to leaders for an absence of self-doubt. Leaders therefore need to show self-confidence in order to convince followers of the rightness of goals and decisions.
5. Intelligence: leaders need to be intelligent enough to gather, synthesize and interpret large amounts of information and to be able to create visions , solve problems and make correct decisions.
6. Job relevant knowledge: effective leaders have a high degree of knowledge about the company, industry, and technical matters, in depth knowledge allows leaders to make well informed decisions and to understand the implications of those decisions. They also show flexibility to deal with various changing stimuli in the environment.
Other traits of a good leader are dependable, fair, objective, sensitive, self-confident, persistent, broad minded, creative, tolerant, calm, insight, enthusiastic, intelligent, courage, visionary…
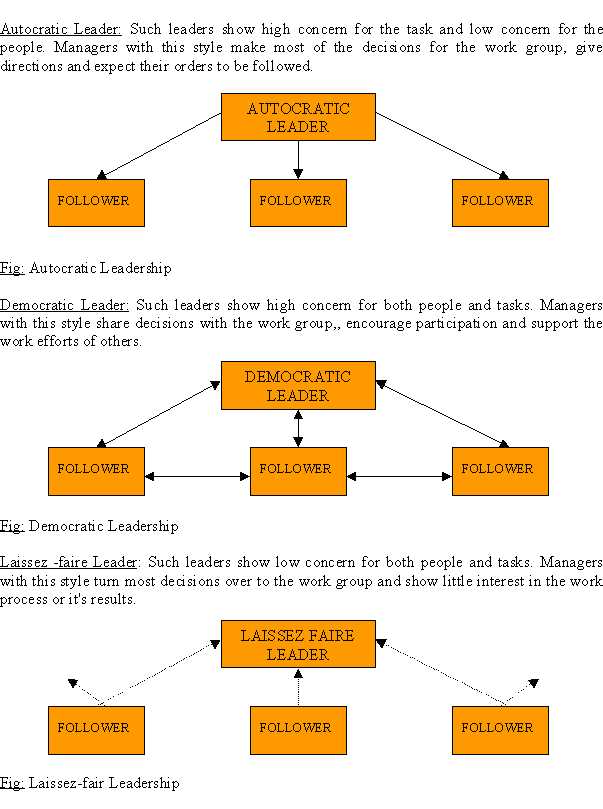
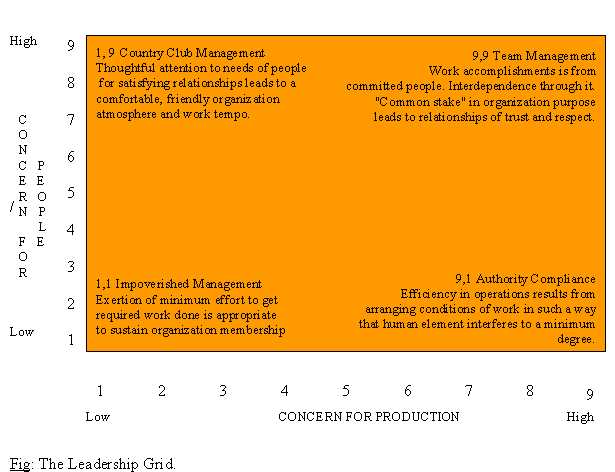
Behavioral Approach: This approach views leadership in terms of the group-maintenance and the task-related activities that a leader has to perform. Thus different leaders will lead differently depending on their relative concern for the people or the concern for production.
On the basis of their differing concerns leaders adopt different styles of leading like:
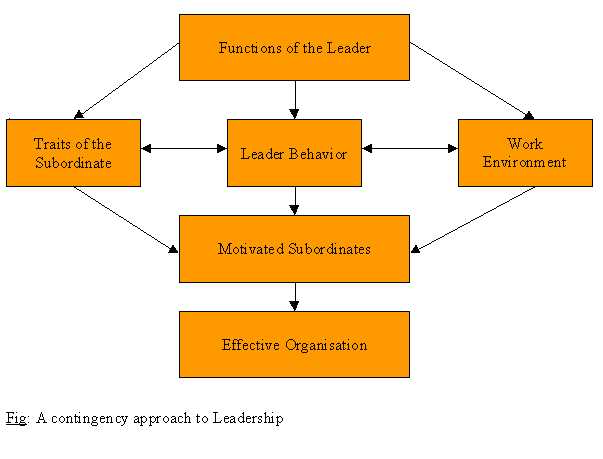
Contingency Approach: This approach views that the leadership style that best contributes to the achievement of the organisational goals might vary in different types of situations. Various factors may influence the "best" leadership style. These factors may include the task requirements, employee's characteristics, expectations and behavior, the organisational
culture and policies etc. A contingency approach to leadership effectiveness is shown below:
Functions and Responsibilities of a Leader
A leader has to perform a variety of functions and responsibilities inorder to achieve group goals. Some of the functions of leader are :
To -
+ Set goals
+ Present positive image of goals and responsibilities
+ Communicate with employees
+ Inspire and Motivate
+ Capitalize on individuals skills and interests of staff
+ Coordination
+ Anticipate needs and problems
+ Establish guidelines and structure
+ Involve staff in decision making
+ Establish favorable conditions for increasing productivity
+ Build sense of security
+ Acknowledge group achievements
Other Issues in Leadership
Transactional Leaders are those who determine what subordinates need to do to achieve objectives, classify those requirements, and help subordinates become confident they can reach their objectives.
Transformational Leaders are those who through their personal vision, energy and inspiration have a major impact on their organisations by working on the SWOT and providing high quality solutions. Example: Jan Carlzon turned Scandinavian Air System from $8 million loss to $ 71 million profit in one year !
Charismatic Leaders develop special leader-follower relationships and inspire followers through their personal charisma. The leader is an idolized hero, a messiah, a savior for the followers. Example: Mahatma Gandhi, John F. Kennedy, Thomas Watson (IBM), Walt Disney.
Post-Heroic Leadership : Make everyone a leader by making them perform with their Head, Heart and Hands. Leadership must permeate the whole organisation and not just with one or two superstars at the top.
Subconscious Leadership: Leadership tendency may emerge as a result of the unfulfilled subconscious desires of a person.
Romantic Leadership: Some are born to be followers and have "fairy tale" concepts of the leader's skills and capabilities.
Substitute Leadership: Does every group need a leader ? Have a professional approach, satisfying job, clear rules and feedback and leader's role diminish and eventually cease to exist.
Leadership across Cultures
Leadership styles may vary over different cultures. European managers tend to be more people oriented than American managers. Japanese cultures is very collective oriented, while American focuses more on profitability. Time horizons also are affected by cultures. US firms often focus on short term efforts. Japanese firms take a longer term outlook. It is essential that international managers are become aware of such cultural differences when leading in a foreign country.
Test Your Knowledge
& _________ is defined as the process of directing and influencing the task related activities of group members.
& Leadership = _______ x ___________
& Leadership involves influencing people by using different types of ________
& ________ is the capacity to affect the attitudes or behavior of others.
& Position power can be classified into _______, __________ and __________.
& _______ is the capacity to influence other people because of specialized knowledge.
& The ________ approach to leadership believes that leadership behavior is the sum total of all the qualities of the leader.
& Three major traits that differentiate leaders from non-leaders are _______, _______ and ________.
& The __________approach views leadership depending on their relative concern for task and people.
& An __________ leader shows high concern for tasks and low concern for people.
& A democratic leader shows high concern for both people and tasks (True or False)
& _____________ leaders show low concern for both people and tasks.
& Leadership style that best contributes to the achievement of the organisational goals might vary in different situations. (Name the approach)
& Inspiring and motivating employees is not the responsibility of the leader. (True or False)
& A ____________ leader brings about major changes in the organisation through their personal vision, energy and inspiration.
& Charismatic leaders cannot influence their followers easily (True or False).
& Leadership styles differ from culture to culture (True or False)